Understanding alzheimer’s dementia brain health
When it comes to brain health and Alzheimer’s, understanding the impact of Alzheimer’s disease on the brain is crucial. alzheimer’s dementia brain health refers to the effects of Alzheimer’s disease on the brain and overall cognitive function. This neurological disorder not only affects memory but also impacts various cognitive abilities, ultimately influencing brain health.
The Benefits of Maintaining Brain Health in Alzheimer’s
Prioritizing brain health in Alzheimer’s disease can have significant benefits. By engaging in activities that stimulate brain function, individuals may experience slower cognitive decline and better overall quality of life. Additionally, maintaining brain health can potentially delay the progression of Alzheimer’s symptoms and enhance cognitive resilience.
Understanding the Brain in Alzheimer’s Disease
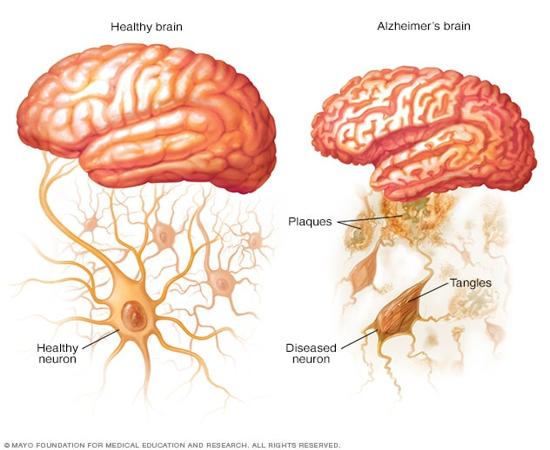
Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by the presence of abnormal protein deposits in the brain, known as amyloid plaques and tau tangles. These deposits disrupt communication between brain cells, leading to cell death and cognitive decline. As the disease progresses, the brain undergoes structural changes that significantly impact memory, thinking, and behavior.
Frequently Asked Questions About alzheimer’s dementia brain health
1. How does Alzheimer’s disease affect the brain?
Alzheimer’s disease disrupts the normal functioning of the brain by causing the accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles. These abnormal protein deposits impair communication between brain cells and lead to widespread neuronal damage.
2. What role does brain health play in Alzheimer’s?
Maintaining brain health through activities like cognitive stimulation, physical exercise, and a healthy diet can support cognitive function and potentially delay the progression of Alzheimer’s symptoms. A healthy brain may also exhibit greater resilience against the effects of the disease.
3. How can dementia and Alzheimer’s affect the brain differently?
While Alzheimer’s disease is a specific type of dementia that primarily affects memory and cognitive function, other forms of dementia can impact different areas of the brain, leading to a variety of cognitive and physical symptoms. Understanding these distinctions is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
4. What are the long-term effects of Alzheimer’s disease on the brain?
Over time, Alzheimer’s disease can lead to progressive brain atrophy, characterized by the shrinkage of brain tissue and loss of neurons. This structural damage contributes to the worsening of cognitive symptoms and eventual decline in overall brain health.
5. How can lifestyle choices impact brain health in Alzheimer’s patients?
Engaging in activities that promote brain health, such as social interaction, cognitive exercises, and a balanced diet, can help support cognitive function in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. By adopting a brain-healthy lifestyle, patients may experience improved quality of life and potentially slower disease progression.
Conclusion
In conclusion, alzheimer’s dementia brain health is a complex and crucial aspect of managing Alzheimer’s disease. By prioritizing brain health through lifestyle choices, cognitive stimulation, and targeted interventions, individuals can potentially mitigate the impact of the disease on their cognitive function. Understanding the effects of Alzheimer’s on the brain and taking proactive steps to support brain health can make a meaningful difference in the quality of life for those affected by this neurological disorder.